Tampa (BLOOM) – If you’ve ever pushed yourself through a challenging workout, chances are you’ve experienced that familiar ache in your muscles afterward. Muscle soreness, also known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), is a common phenomenon that many athletes and fitness enthusiasts encounter.
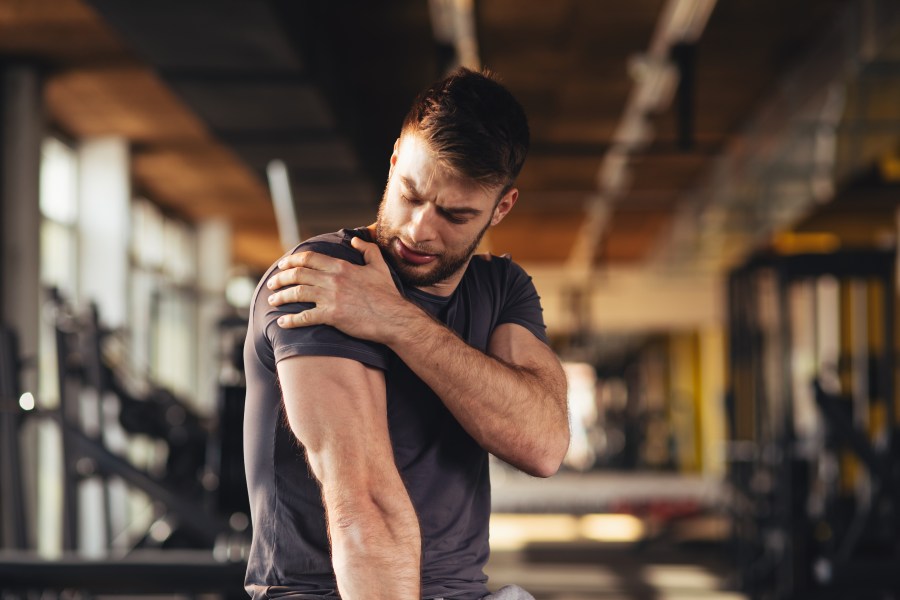

The Physiology of Muscle Soreness
To understand why our muscles get sore, it’s essential to grasp the underlying physiology. One theory suggests that muscle soreness is a result of microscopic damage to muscle fibers during exercise. This damage triggers an inflammatory response, leading to swelling and pain. Additionally, the activation of pain receptors and increased nerve sensitivity contribute to the overall sensation of soreness.
Surprising Causes of Muscle Soreness
While exercise itself plays a significant role in muscle soreness, there are some surprising causes worth exploring. Eccentric exercise, which involves lengthening contractions, tends to induce more soreness than concentric exercise. During eccentric movements, such as the downward phase of a squat or the lowering of weights, muscles experience greater tension and stress, leading to increased soreness.
Microscopic muscle tears are another surprising cause. Even though they sound alarming, these tiny tears are a natural response to exercise. As you challenge your muscles, these micro-tears occur and contribute to the soreness you feel post-workout.
Metabolic waste accumulation, including lactic acid, has long been associated with muscle soreness. However, recent research suggests that lactic acid may not be the primary culprit. Instead, it is believed that other metabolic byproducts and substances released during exercise contribute more significantly to muscle soreness.
Factors Affecting Muscle Soreness
Several factors influence the intensity and duration of muscle soreness. The intensity and duration of your exercise play a crucial role. Longer, more intense workouts tend to result in more pronounced soreness. Additionally, your training status and muscle adaptation play a part. As you continue to train, your muscles adapt and become more resistant to soreness over time.
It’s also important to note that individual differences play a role in muscle soreness. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to feeling more soreness, while others may have variations in pain perception. So, don’t be surprised if your workout buddy experiences less soreness than you, even if you did the same workout.
Remedies for Muscle Soreness
Now that we understand the causes, let’s explore some effective remedies to help alleviate muscle soreness and speed up recovery. Active recovery is an excellent strategy that involves engaging in light exercise, such as a gentle walk or swim, to increase blood flow and promote the removal of metabolic waste.
Contrast therapy, alternating between cold and hot treatments, can also aid in reducing inflammation and relieving muscle soreness. Taking a contrast shower or using ice packs and warm towels can be beneficial.
Proper nutrition and hydration are often overlooked but are crucial for optimal muscle recovery. Fueling your body with nutrient-dense foods and staying well-hydrated supports muscle repair and minimizes soreness.
Massage and foam rolling are popular techniques to ease muscle tension and soreness. Gentle self-massage or using a foam roller can help break up adhesions and knots in your muscles, promoting better blood flow and faster recovery.
Over-the-counter remedies such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or topical creams can provide temporary relief from muscle soreness. However, it’s important to use them sparingly and consult a healthcare professional if soreness persists or worsens.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention is always better than cure, so let’s explore some strategies to minimize muscle soreness in the first place. Prior to your workout, be sure to warm up properly and gradually increase the intensity of your exercise. A good warm-up routine prepares your muscles for the upcoming exertion and reduces the risk of excessive soreness.
Similarly, cooling down after your workout with light stretching and low-intensity movements helps your muscles transition into a state of relaxation, minimizing post-workout soreness.
Maintaining proper form and technique during exercise is also crucial. Poor form can place excessive strain on certain muscles, leading to increased soreness. Focus on maintaining proper alignment and seek guidance from a qualified trainer if needed.
Managing Chronic Muscle Soreness
It’s important to differentiate between acute muscle soreness, which typically lasts a few days, and chronic muscle soreness that persists for an extended period. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe muscle soreness that hinders your daily activities, it’s advisable to seek medical advice. Chronic soreness could be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires attention.
Understanding the surprising causes behind muscle soreness empowers you to take proactive steps in managing and recovering from it. Remember, everyone’s body responds differently, so finding the remedies that work best for you may require some experimentation. By listening to your body, taking care of your muscles, and incorporating effective recovery strategies, you can minimize muscle soreness and optimize your training journey.
Recent Scientific Studies on the Causes and Mechanisms of Muscle Soreness

Advancements in scientific research have deepened our understanding of the causes and mechanisms behind muscle soreness. Here are some recent studies that shed light on this topic:
- Study: “Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: Effects on Muscle Morphology and Intramuscular Proteins” (Published in the Journal of Applied Physiology, 2021)
This study examined the impact of eccentric exercise on muscle damage and the subsequent development of soreness. The findings revealed that eccentric exercise leads to structural changes in muscle fibers and an increase in intramuscular proteins associated with inflammation and pain perception. These insights highlight the importance of eccentric exercise as a significant contributor to muscle soreness.
- Study: “Metabolic Stress and Inflammatory Response in Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: Mechanisms and Adaptations” (Published in Frontiers in Physiology, 2022)
This review article explores the role of metabolic stress and the inflammatory response in exercise-induced muscle damage and subsequent soreness. It highlights how metabolic byproducts, such as reactive oxygen species and cytokines, contribute to the inflammatory process and the perception of pain. The study emphasizes the complex interplay between metabolic stress, inflammation, and muscle soreness.
- Study: “Genetic Factors Influence Muscle Soreness and Recovery Following High-Intensity Exercise” (Published in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 2021)
Examining the influence of genetic factors on muscle soreness, this study investigated the role of specific genetic variants related to pain perception and inflammation. The findings revealed that individuals with certain genetic variations experienced different levels of muscle soreness and recovery following high-intensity exercise. This study highlights the importance of considering individual genetic differences in understanding and managing muscle soreness.
- Study: “Acute Exercise-Induced Inflammation and Its Impact on Skeletal Muscle Adaptations” (Published in Exercise Immunology Review, 2022)
This review article focuses on the acute inflammatory response triggered by exercise and its implications for muscle adaptations. It discusses how exercise-induced inflammation plays a dual role in muscle soreness and subsequent muscle remodeling and adaptation. Understanding this relationship can provide valuable insights into optimizing recovery strategies and maximizing the benefits of exercise.
These recent scientific studies contribute to our knowledge of the causes and mechanisms of muscle soreness. By investigating factors such as eccentric exercise, metabolic stress, genetic influences, and the inflammatory response, researchers are uncovering the intricate processes that contribute to post-workout soreness. Incorporating these findings into our understanding can inform the development of more effective strategies for managing and recovering from muscle soreness.
Links and References
Here are some helpful resources and references to further explore the topic of muscle soreness:
- American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM): The ACSM provides valuable insights and guidelines on exercise, including information on muscle soreness and recovery.
- PubMed: A comprehensive database of scientific research articles. Searching for keywords like “muscle soreness” or “DOMS” will yield numerous studies on the topic.
- National Strength and Conditioning Association (NSCA): The NSCA offers a wide range of resources for strength and conditioning professionals, including articles and journals that cover muscle soreness and recovery strategies.
- American Council on Exercise (ACE): ACE provides fitness professionals and enthusiasts with evidence-based resources, articles, and educational materials, including information on muscle soreness management.
- Sports Medicine Australia (SMA): SMA offers practical resources and information on various sports medicine topics, including muscle soreness and recovery techniques.
- Harvard Health Publishing: The Harvard Medical School’s consumer health division provides reliable and accessible health information, including articles on exercise-related topics, muscle soreness, and recovery.
Remember to consult with qualified healthcare professionals, trainers, or coaches for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.